sacral test torsion|sacral torsion self treatment : trade If a sacral dysfunction occurs along an oblique axis, it is considered a torsion, with the oblique axis located at the sacral base opposite the "stuck" side of the sacrum. In other . In Theaters At Home TV Shows. The team behind the biggest multiplayer video game of all time is tasked with building worlds, molding heroes and creating legends, but the most .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webSee more questions & answers about this hotel from the Tripadvisor community. Garden Motel in Franca, SP: View Tripadvisor's unbiased reviews, photos, and special offers for .
How to identify and treat sacral torsion, sacral shear, and related mechanical chronic low back pain and buttock pain.If the test is negative (improved symmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral flexion dysfunction or an anterior sacral torsion. If the test is positive (worsened asymmetry of the bases), this indicates a sacral extension dysfunction or a . If a sacral dysfunction occurs along an oblique axis, it is considered a torsion, with the oblique axis located at the sacral base opposite the "stuck" side of the sacrum. In other .Spring Test 1. Find sacral base 2. Place heel of hand over Lumbosacral junction 3. Spring in an Anterior motion 4. Results: a. Positive test = If there is NO springing allowed = Non-neutral .
A sacral torsion is a pattern of traumatic, symptomatic, sacral asymmetry with altered movement in the joint. It is described in many works on osteopathic-based biomechanics of the SIJ,While attempting to rule out other causes of low back pain, provocation tests such as FABRE, distraction, thigh thrust, sacral compression, Gaenslen’s, and sacral thrust can be a useful .
Lack of understanding of common causes of SI joint pain may lead to the misdiagnosis and mistreatment of SI joint dysfunction. Over the past 37 years, Shealy has noted that at least 15% of patients coming to his clinic for . To review and further discuss the validity of some of the mostly used clinical provocation tests such as Distraction test, Thigh Thrust test, Compression test, Sacral Thrust .
what causes sacral torsion
The seated flexion test is used to detect sacroiliac joint (SIJ) dysfunction. SIJ dysfunction can be a source of pain in the lower back and buttocks.[1] Toggle navigation. p Physiopedia; p Physiopedia . The test is negative if the movement of the PSISs was symmetrical or positive if one side moved more than the other in the cephalic and/or .Once I started using the stork test again, I realized how many sacral fixations I was missing, and that my previous corrections didn't always correct the fixation. I am once again using this model daily. Top: Position for correction of left .Sacroiliac joint pain commonly occurs because of anatomic disruption within the joint. Sacroiliac jo . Restricted range of motion in the SIJ causing a torsion, flexion, extension motion pattern. . Upon examination, there is a negative straight leg raise test, but positive thigh thrust, sacral distraction, and sacral compression tests and .
Sacral motion described in relation to the L5 vertebra. Sacral torsion or sacral rotation on an oblique axis; Sacral shears (unilateral sacral flexion or extension) Bilateral sacral flexion or extension; Sacral motion described in relation to the ilium. Anterior sacrum. The sacral base rotates forward and sidebends to the opposite side of the .
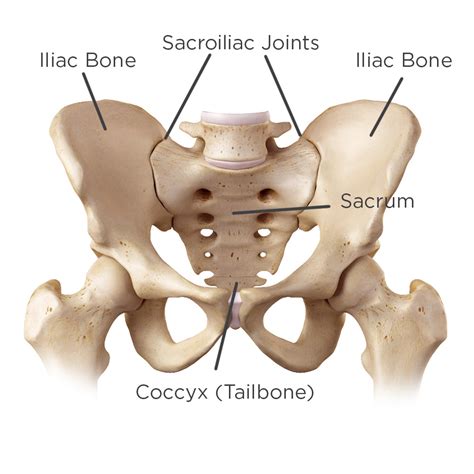
Sacroiliac (SI) joint injury is a common cause of low back pain. Posterior pelvic joint pain a common name for SI joint dysfunction. The spine and pelvis are connected by the sacroiliac joint. The SI joint lies between the iliac's articular surface and the sacral auricular surface. When an injury occurs to the SI joint, patients often experience significant pain in their . Dr. Whelton is a physical therapist who developed several breakthrough treatment methods for immediate pain relief. He has made numerous orthopedic discoveri.Sphinx position involves having the patient lie prone, then prop themselves up on their elbows to extend the lumbar spine and flex the sacrum (Figure 1).This can be very uncomfortable for extended or backward torsion sacral dysfunctions. See "Diagnosing sacral somatic dysfunction." Sims position is a modified version of lateral recumbent. Have the patient lie in the lateral . Chapter 2 Common presentations and diagnostic techniques Chapter Contents The sacroiliac joint Anatomy, development and aging SI joint mobility Axes of motion Biomechanics Trunk flexion Trunk extension Landing on one leg Vertical forces on the sacrum Ambulation Kinetic function and stability Panjabi: active, passive and neural control systems .
The sacroiliac joints are located on each side of the spine between the two pelvic bones, which attach to the sacrum. The main function within the pelvic girdle is to provide shock absorption for the spine and to transmit forces between the upper body and the lower limbs. The SI joint experiences forces of shearing, torsion, rotation, and tension. Ambulation is heavily impacted . A look into the evaluation and treatment of sacral torsion's using an Osteopathic approach with muscle energy techniques.Sacral plexus: derives from L4-S4 nerve roots; sits on the internal surface of the piriformis muscle; most of the sacral nerves stemming from the sacral plexus exit through the greater trochanteric notch; the sciatic nerve forms out of sacral plexus and may be compressed by muscle, causing radicular pain down the leg; Coccygeal plexus
P a g e | 2 Hesch Institute March 2012 www.Heschinstitute.org Email: [email protected] ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS I would like to thank our Creator, my parents Reuben and Bernadine Hesch (both deceased) forStudy with Quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like Upon examining the posterior landmarks of a patient's pelvis, you find the following: deep left sacral sulcus, left inferior/posterior ILA, right positive seated flexion test. Your diagnosis is? a. Left on right sacral torsion b. Left unilateral sacral extension c. Right unilateral sacral extension d. Right on left sacral torsion .Gaenslen's Test (Gaenslen's maneuver) is one of the five provocation tests that can be used to detect musculoskeletal abnormalities and primary-chronic inflammation of the lumbar vertebrae and Sacroiliac joint (SIJ). The subsequent tests include; the Distraction Test, Thigh Thrust Test, Compression Test and the Sacral Thrust Test.
Lumbar / sacral nerve involvement: The nerves of the lumbar and sacral plexus normally are able to slide in and out of the IVF and sacral foramina with the movements of the lower extremity. 3 When they don't, the sacrum and coccyx .
4. THE SACRUM The sacrum, is a large triangular bone at the base of the spine that forms by the fusing of sacral vertebrae S1–S5 , between 18 and 30 years of age. The sacrum is situated at the upper, back part of the pelvic .
The data do not support the value of these tests in identifying innominate torsion, although the use of these tests for identifying other phenomena (eg, sacroiliac joint hypomobility) cannot be ruled out. Further exploration of the association of Gillet test .Left on Right Posterior Sacral Torsion -- L5 NonAdaptive (FRSright) Non-neutral dysfunctions at L5 (FRSright) often accompany a left on right sacral torsion.An FRSright at L5 can be identified when the patient is backward bent and L5 appears rotated right when compared to a left rotated and right sidebent sacrum.. In the neutral position, when the sacrum is side bent right and . The sacrum contributes to several musculoskeletal and visceral health conditions. The spinal segment plays a primary role in the transmission of weight throughout the gait cycle, sitting, and standing.[1][2] It also houses the sacral nerves, which provide autonomic innervation to many of the lower abdominal and pelvic organs. It has long been a belief that the autonomic .
A frequently reported sacral movement dysfunction is named sacral torsion about an oblique axis, which is also known as sacral torsion, or simply as torsion. Torsions do meet the above definition of SIJD, and are the focus of this chapter. TORSION THEORY A sacral torsion is a pattern of traumatic, symptomatic, sacral asymmetry with altered movement仙骨スラストテスト(Sacral thrust) ゲンスレンテスト(Pelcic Torsion)その①; ゲンスレンテスト(Pelcic Torsion)その② ※最初の4つのテストのうち2つ、あるいは6つのテストのうち3つが陽性であれば、仙腸関節性の可能性が高い。
sacroiliac joint picture diagram
Thomas test – one hip flexed to flatten the lumbar spine, other leg relaxed to table. • Normal: hip flexion = 0 degrees, no hip ABD/ADD, and knee flexion = 75 degrees. . (i.e. anterior vs. posteriorly rotated ilium, right vs. left sacral torsion, etc.) that is often taught in most SIJ courses. However, since the individual tests .
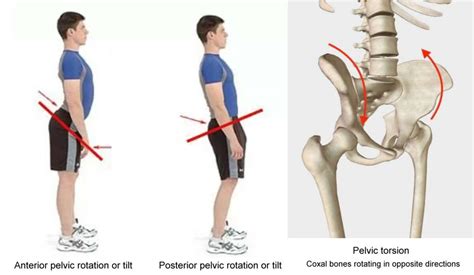
The evidence on the amount and direction of sacroiliac motions in a variety of test positions is largely contradictory. Conclusions This review of the literature demonstrates that there tends to be, although certainly not invariably, posterior innominate rotation on the side of . After watching this video you will be able to:1. Describe Symmetrical vs Asymmetrical Sacroiliac Joint Movement2. Describe Nutation as the movement of the Sa. The patterns of muscle tension involved in pelvic torsion (twisted pelvis) On the side of the pelvis in which the coxal bone is tipped forward in anterior rotation, the hip flexors are chronically tight. The primary hip flexors are the psoas major, iliacus, and rectus femoris, which are assisted by the pectineus, sartorius, and tensor fasciae latae.. On this side, the muscles .
This is presented by Dr. Jerry Hesch, MHS, PT, DPT of Hesch institute in Aurora, Colorado. Jerry treats chronic pain using a whole-body Manual Therapy and ed. Pelvic torsion is known to associate with either the left or right innominate bones (ilia) (see the diagram below) that rotate in an opposite direction around a horizontal axis. This axis runs through a landmark called the symphysis pubis shown by Pitkin and Pheasant in 19362. . manipulating the sacroiliac joint (the client may hear a click .
ac test manifold seal kit
sacral torsion treatment
webRonaldo não especificou se aceita convênios. Sugerimos que entre em contato para se informar se o seu convênio é aceito ou se você deve agendar de maneira particular. Você é Ronaldo Coutinho Seixo de Brito Junior? Se cadastre e atualize as informações.
sacral test torsion|sacral torsion self treatment